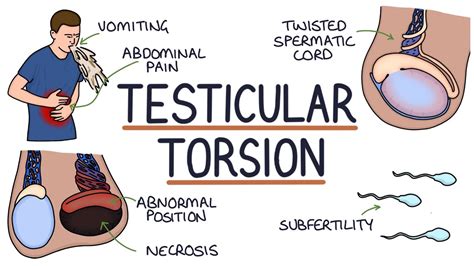
testis torsion test|how to diagnose testicular torsion : discount store Testicular torsion is the twisting of the spermatic cord within the scrotum. It is a urological emergency requiring urgent surgical intervention . It can either be due to an intravaginal (‘bell-clapper deformity’) or extravaginal cause.
Resultado da Informações sobre CaliFit Academia - Unidade Cachoeirinha, Academia em Manaus (Amazonas) Aqui você encontra a localização, horário de .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEB22 de mar. de 2023 · ★BIG WIN!!★ FINALLY A BONUS!! 😱 OCEAN MAGIC GRAND Slot Machine (IGT). Can it be??? YES!!! My first ever OCEAN MAGIC bonus and it was bubblicious! ALBERT'S S.
Prehn's sign is a clinical finding that helps clinicians determine whether testicular pain is caused by epididymitis or testicular torsion. A positive Prehn's sign, characterized by pain relief from the maneuver, is indicative of .
Doctors often diagnose testicular torsion with a physical exam of the scrotum, testicles, abdomen and groin. Your doctor might also test your reflexes by lightly rubbing or .
Testicular torsion is a clinical diagnosis, and patients typically present with severe acute unilateral scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Physical examination may reveal a high-riding. Testicular torsion occurs when the testicle rotates on the spermatic cord, which brings blood to the testicle from the abdomen. If the testicle rotates several times, blood flow to .Testicular torsion is an emergency condition due to rotation of the testis and consequent strangulation of its blood supply. Symptoms are acute scrotal pain and swelling, nausea, and vomiting. Diagnosis is based on physical .
Testicular torsion is the twisting of the spermatic cord within the scrotum. It is a urological emergency requiring urgent surgical intervention . It can either be due to an intravaginal (‘bell-clapper deformity’) or extravaginal cause. Testicular torsion is a time-dependent diagnosis, a true urologic emergency, and early evaluation can assist in urologic intervention to prevent testicular loss. Ultrasound is the .Testicular torsion causes sudden, severe pain and later swelling of the affected testis. A doctor's examination and sometimes ultrasonography are needed for testicular torsion diagnosis. Treatment is to untwist the spermatic cord. Testicular torsion is a urological emergency caused by the twisting of the testicle on the spermatic cord leading to constriction of the vascular supply, time-sensitive ischaemia, .
testicular torsion signs on examination
Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord (from which the testicle is suspended) twists, cutting off the blood supply to the testicle. [3] The most common symptom in children is sudden, severe testicular pain. [1] The testicle may be higher than usual in the scrotum and vomiting may occur. [1] [2] In newborns, pain is often absent and instead the scrotum may become . Testicular torsion refers to the torsion of the spermatic cord structures and subsequent loss of the blood supply to the ipsilateral testicle. . Menon VS, et al. Transscrotal Near Infrared Spectroscopy as a Diagnostic . Investigations. The diagnosis of testicular torsion is a clinical one, therefore any suspected cases should be taken straight to theatre for scrotal exploration.. However, in cases with sufficient equipoise, Doppler ultrasound .
testicular torsion signs and symptoms
American Urological Association Curriculum on Acute Scrotum: This case-study offering from the association's medical school curriculum covers the differential diagnosis of acute scrotum with a concentration on 6 conditions: epididymitis, hernia, scrotal trauma, testicular torsion, testicular tumor, and torsion of testicular appendices. Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord becomes twisted. This causes a restriction in blood flow to the testes, severe pain, and possibly permanent damage. Find out what causes this .
Testicular torsion is the twisting of a testis on its spermatic cord so that the blood supply to the testis is blocked. Testicular torsion causes sudden, severe pain and later swelling of the affected testis. A doctor's examination and sometimes ultrasonography are needed for testicular torsion diagnosis. Treatment is to untwist the spermatic cord.Testicular torsion is an emergency: When it happens, a guy needs surgery — fast. . abdomen, and groin and might test your reflexes by rubbing or pinching the inside of your thigh. This normally causes the testicle to contract, which probably won't happen if you have a .
Testicular torsion is a twisting of the spermatic cord and its contents and is a surgical emergency affecting 3.8 per 100,000 males younger than 18 years annually. It accounts for 10% to 15% of Each year, testicular torsion affects one in 4,000 males younger than 25 years. Early diagnosis and definitive management are the keys to avoid testicular loss. All prepubertal and young adult .1: Epididymis 2: Head of epididymis 3: Lobules of epididymis 4: Body of epididymis 5: Tail of epididymis 6: Duct of epididymis 7: Deferent duct (ductus deferens or vas deferens). Prehn's sign (named after urologist Douglas T. Prehn) [1] is a medical diagnostic indicator that was once believed to help determine whether the presenting testicular pain is caused by acute .
Testicular torsion occurs in teenage boys aged 13-18 years. This is found to happen in around 1 in 4,000 young men. Newborn babies and younger children sometimes develop this problem. It is uncommon over the age of 25 but does occur sometimes in older adults and can occur at any age.Testicular torsion has an annual incidence of approximately 1 in 4,000 males younger than 25 years. 1 It is more common in children and adolescents, and delayed repair can result in the loss of .↑ Blaivas, M, et al. Emergency evaluation of patients presenting with acute scrotum using bedside ultrasonography. Academic Emergency Medicine. 2001; 8(1):90-93. ↑ Barbosa, JA, et al. Development of initial validation of a scoring system to diagnose testicular torsion in children. The Journal of Urology. 2013; 189:1853-8. ↑ Gordon J, Rifenburg RP. . Spermatic Cord .
Testicular torsion is when the spermatic cord above your testicle twists, cutting off blood flow to your testicle. Testicular torsion can happen at any age, but it most often happens to boys ages 12 to 18 or babies. Without blood supply, the tissue of your testicle can die in a few hours . See a doctor right away if you think you have .Testicular torsion can occur at any age but commonly occurs soon after birth or between the ages of 12–18 years with a peak in incidence at age 13–14 years. . With regards to the intraoperative bleeding test, all patients with grade 3 bleeding (major bleeding that requires multiple hemoclips and sessions of hemocoagulation) required . The cremasteric reflex has been reported to be absent in 100% of cases of testicular torsion, making it a potentially useful sign in this diagnosis. However, a significant number of case reports and small case series exist, demonstrating that the test is not 100% specific, and the reflex can be present in cases of testicular torsion.
wholesale softness tester factories
The test can show if you have testicular torsion. Testicular torsion is a twisting of the testicle that can cut off blood flow. If ultrasound with color Doppler shows lower blood flow to a testicle than is typical, the testicle is twisted. If blood flow is higher than typical, this can help confirm that you have epididymitis.
A diagnosis of testicular torsion should be suspected in any person presenting with acute scrotal pain and/or swelling, before other causes are considered.. Ask about:. Any scrotal pain — the location (including unilateral or bilateral), nature, radiation to surrounding structures, speed of onset, duration, severity, exacerbating factors (such as activity or positional changes).Ultrasound imaging is a noninvasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. It is safe and painless. It produces pictures of the inside of the body using sound waves. . Ultrasound can identify testicular torsion, the twisting of the spermatic cord that contains the vessels that supply blood to the testicle . Testicular torsion, or twisted testicle, can be extremely painful. . A healthcare professional may also test the patient’s cremasteric reflex, which is highly effective in helping diagnose .
This video contains a visual explanation of testicular torsion, aimed at helping students of medicine and healthcare professionals prepare for exams. Written.
Testicular torsion refers to the torsion of the spermatic cord structures and subsequent loss of the blood supply to the ipsilateral testicle. This is a urological emergency; early diagnosis and treatment are vital to saving the testicle and preserving future fertility. . A Prospective Comparison to Gold Standard Diagnostic Test Study. J Urol . Testicular torsion is a very serious condition and is considered a medical emergency. Rotation of the testicle around the spermatic cord can cause obstruction of the arterial blood flow to the testicle, as well as the venous blood outflow, which can ultimately lead to necrosis or death of the testicular tissue.
4. Discussion. Testicular torsion is a well known urologic emergency that needs to be diagnosed and treated rapidly for the salvage of testis. It was first described in 1840 by Delasiauve, and this happened to be in a 15-year-old boy with UDT .. A UDT may be located in the abdomen, the inguinal canal, the superficial inguinal pouch, and the upper scrotum.
Testicular torsion is a painful twisting of a boy’s testicles and spermatic cord. Torsion causes blood to not flow to the testicles. This can damage them. Treatment needs to be done right away to prevent long-lasting (permanent) injury to the testicles. . Know why a test or procedure is recommended and what the results could mean. Testicular torsion is a urologic emergency caused by the twisting of the testicle on the spermatic cord leading to constriction of the vascular supply, time-sensitive ischemia, and/or necrosis of testicular tissue. Laher A, Ragavan S, Mehta P, et al. Testicular torsion in the emergency room: A review of detection and management strategies.
It is the imaging modality of choice across all age groups when ruling out testicular torsion, particularly duplex examination including color and spectral Doppler sonography, with sensitivity and specificity both approaching 100%. US can also detect other entities that may mimic symptoms of testicular torsion, including epididymo-orchitis .
testicular torsion prognosis
3 semanas: 5-50 mlU/ml 4 semanas: 4-426 mlU/ml 5 semanas: 19-7.340 mlU/ml 6 semanas: 1.080-56.500 mlU/ml 7 – 8 semanas: 7.650-229.000 mlU/ml 9 – 12 semanas: 25.700 . Ver mais
testis torsion test|how to diagnose testicular torsion